Most humans live in hydrographic basins, because water is essential, but we are exhausting the systems that give us life. Danubius RI provides multi-disciplinary data on how river waters, and the activities of humans upstream, impact the coastal waters that receive them.
Continue readingThe Integrated Carbon Observation System
ICOS ERIC provides the scientific community with high-quality data and measurements in all the different components of the Earth – changing concentrations in greenhouse gases and exchanges between the atmosphere and the ocean and between the atmosphere and the terrestrial biosphere.
Continue readingThe European Multidisciplinary Seafloor and Water Column Observatory
Cristina di Muri from the Italian National Research Council, CNR, talks about the innovative role of the ‘Biodiversity Data Journal’ in publishing data papers and service papers
Continue readingLifeWatch Slovenia: new website launched
The new LifeWatch Slovenia website is online since 31 May 2023. It provides biodiversity and ecosystem researchers with facilities, data resources, web services and Virtual Research Environments. LifeWatch Slovenia remains fully integrated with LifeWatch ERIC in facilitating open data sharing, aggregation and modelling. Besides that, it offers immediate access to national priority projects, as in the case of karst groundwater habitat research and conservation of that national symbol, Proteus anguinus, the only exclusively cave-dwelling aquatic salamander in Europe.
In 2022, the Government of the Republic of Slovenia adopted the Research Infrastructure Roadmap 2030 (NRRI 2030) in which LifeWatch was listed as a priority area in the field of Sustainable Energy and Environmental Technologies. LifeWatch-SI is also part of the Slovenian Strategy for Smart Specialisation (S4) and Horizon 2020, focusing on the development of technological solutions in the field of biodiversity and socio-ecological research.
Since 2015, the Slovenian Consortium has been promoting the importance of integrating and networking information and data to:
- Coordinate biodiversity research in marine, freshwater and terrestrial ecosystems;
- Plan common access to a vast array of data from various sources and observatories;
- Predict computing capabilities with analytical and modelling tools in virtual laboratories; and
- Support training and educational programs that will enable a proper understanding of biodiversity.
The LifeWatch Slovenia Consortium consists of the ZRC SAZU Karst Research Institute, the National Institute of Biology, the Slovenian Forestry Institute, the Slovenian Natural History Museum, the Škocjan Caves Park, the Tular Cave Laboratory, the University of Ljubljana, the University of Maribor, the University of Nova Gorica, and the University of Primorska. Of these, ZRC SAZU serves as the national coordinator and headquarters of LifeWatch-SI.
For more information, please explore the lifewatch.si website.
Environmental Research Infrastructures: LifeWatch ERIC
Cristina di Muri from the Italian National Research Council, CNR, talks about the innovative role of the ‘Biodiversity Data Journal’ in publishing data papers and service papers
Continue readingLifeWatch ERIC at the Congress of the Italian Society of Marine Biology
From 12 to 15 June, the 52nd Congress of the Italian Society for Marine Biology (S.I.B.M.) took place. The Science Department at the University of Messina hosted it a few steps away from the Strait of Messina.
Alessia Scuderi, our Marine Megafauna Scientific Assistant, contributed an account of the Alborán project. Her ‘Cetaceans and maritime traffic in the Strait of Gibraltar: difficult but possible coexistence‘ presentation explored the vulnerability of species streams.
The LifeWatch Alborán project monitors flora, fauna and pollution of the marine and terrestrial environments, protecting and promoting biodiversity. The project is also highly inclusive and participatory, involving the scientific community, citizens and public administrations. It focuses on the Málaga coast in Andalusia, Spain.
The role of LifeWatch ERIC in Alborán is to provide electronic services and the construction of a Virtual Research Environments that contribute to the Global Biodiversity Information Facility network and promote the Smart City Cluster.
The SIBM congress – which featured personalities such as the Rector of the University of Messina, Salvatore Cuzzocrea, the Director of Biomorph, Sergio Baldari; and the Director of Chibiofaram, Sebastiano Campagna – was structured around four themes:
- Extreme environments: new frontiers, resources and threats
- Possible biotechnological applications of marine organisms: from bioactive molecules to bioremediation
- History of Italian marine biology, and
- Vulnerability of species, habitats and resources in the coastal marine environment.
The Italian Society of Marine Biology is a Not-For-Profit organisation, founded in 1969, dedicated to the protection and enhancement of nature and the environment, with particular emphasis on study and scientific research in the marine and coastal environment.
Publications in the Biodiversity Data Journal
Cristina di Muri from the Italian National Research Council, CNR, talks about the innovative role of the ‘Biodiversity Data Journal’ in publishing data papers and service papers
Continue readingAneris Genomic Technologies workshop sets project parameters.
The ANERIS consortium, whose vision is to protect marine and coastal biodiversity through technological and scientific innovation, held a workshop at the InnocOcean Campus of the Flanders Marine Institute in Ostend, Belgium, 30-31 May 2023. The purpose of the two days was to explore the available genomic workflows currently used by the participating ERICs and associated partners and to share experiences.
Officially launched under the Horizon Europe programme on 21 March this year, ANERIS – whose 25 project partners from 13 different countries include LifeWatch ERIC – is coordinated by the Spanish Institut de Ciènces del Mar. At a time when marine and coastal biodiversity are under serious threat because of human activities, climate change and other factors, the four-year ANERIS research project seeks to protect these ecosystems by creating, testing and implementing the next generation of scientific tools and methods for marine life-sensing and monitoring.
LifeWatch ERIC’s participation in the Genomic Technologies workshop consisted of CEO Christos Arvanitidis and International Initiatives & Projects Manager, Cristina Huertas presenting a study and sampling design, including different hypotheses of which marine communities could be considered (e.g. intertidal, planktonic, benthic), which components to include (i.e. molecules), what type of information to collect, the scale of the sampling, etc..
These would be applied to two case studies within ANERIS project, by integrating learnings from previous initiatives, and connecting with other EU projects (Marbefes, Marco Bolo, BioDT,) and Open Science databases (WoRMS, GBIF). They also contributed to other discussions during the workshop on bioinformatics, sampling and the wet labs protocols.
LifeWatch ERIC and GBIF join forces in support of the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework
LifeWatch ERIC and the Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF) are meeting from 30 May to 2 June, 2023, to support the Kunming-Montreal package of decisions adopted by the Parties to the Convention on Biological Diversity, approved at the UN Biodiversity Conference in Montreal, in December 2022.
Continue readingBioinspired robots in Lecce: MAPWORMS Plenary meeting
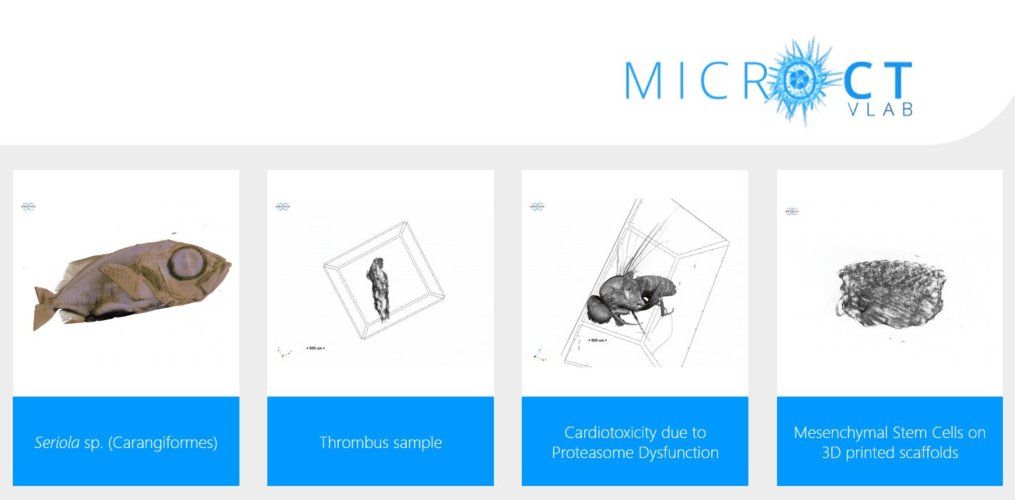
Micro-CTvlab and MedOBIS Repository were present at the plenary meeting of the MAPWORMS project in Lecce, on 15-16 May 2023. MAPWORMS is a Horizon Europe project which aims to propose robots that are inspired by simplified forms of marine Annelida, able to perform tasks in response to environmental stimuli, thus adapting to the working environment with a shape-morphing strategy with unique features in terms of powering and eco-friendliness.
Micro-computed tomography (micro-CT) is being used to visualize the morphological and anatomical features of the annelids. These data will also be used to create a virtual gallery in the Micro-CTvlab, a virtual laboratory which was developed during the LifeWatch Greece project and offers virtual galleries and online tools for the 3D manipulation of micro-CT datasets.
Furthermore, distributional/georeferenced data produced during the MAPWORMS project, will be deposited in the MedOBIS Repository, which is the Mediterranean Node for OBIS and is hosted by the IMBBC, HCMR in Crete. Its development started in 2003, and it was operational by 2005 as a Tier 3 of EurOBIS. Under the European projects EMODnet Biology and LifeWatchGreece, it became a Tier 2 node and extended to cover the entire Mediterranean Sea. Mrs Dimitra Mavraki has been appointed as the Data Manager of the MAPWORMS project, and presented the Data Management Plan, in which several FAIR repositories, including MedOBIS, have been proposed to the partners in order to deposit their data.
The MAPWORMS project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon Europe research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 101046846.