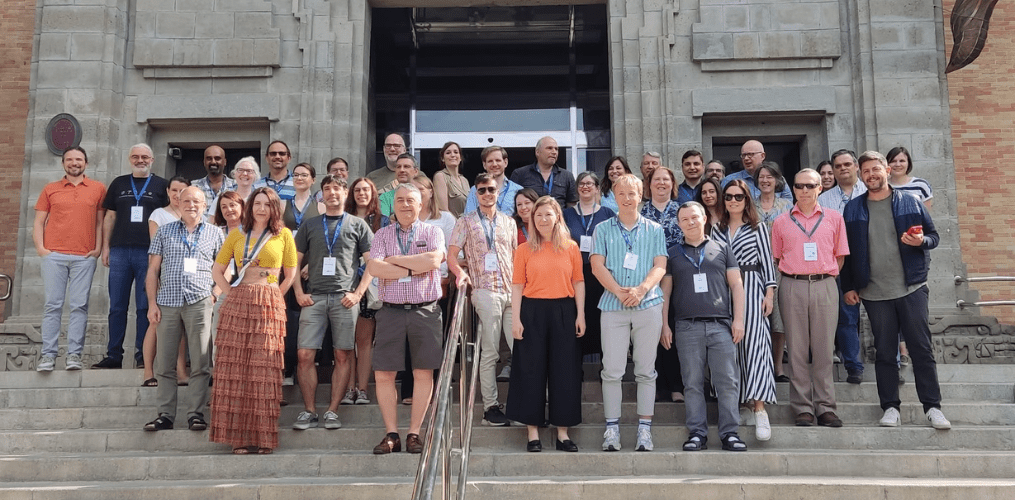
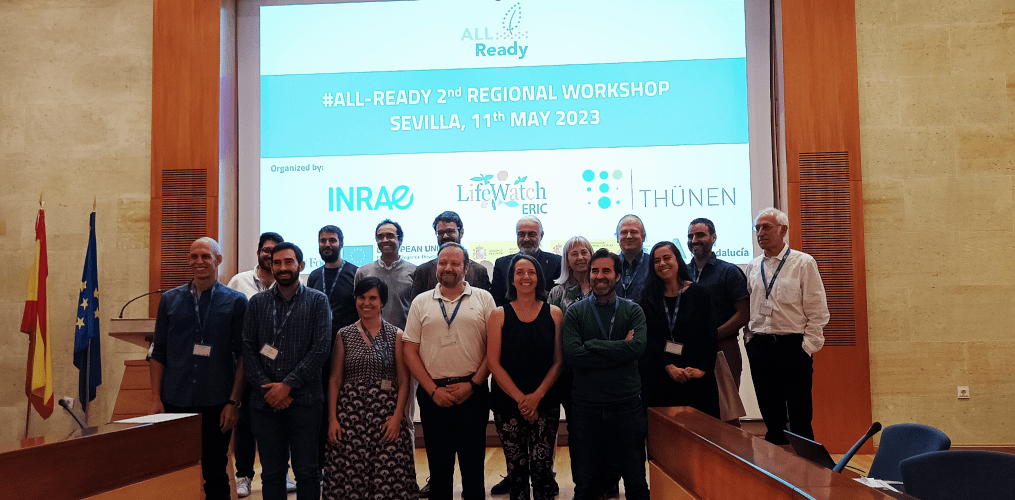
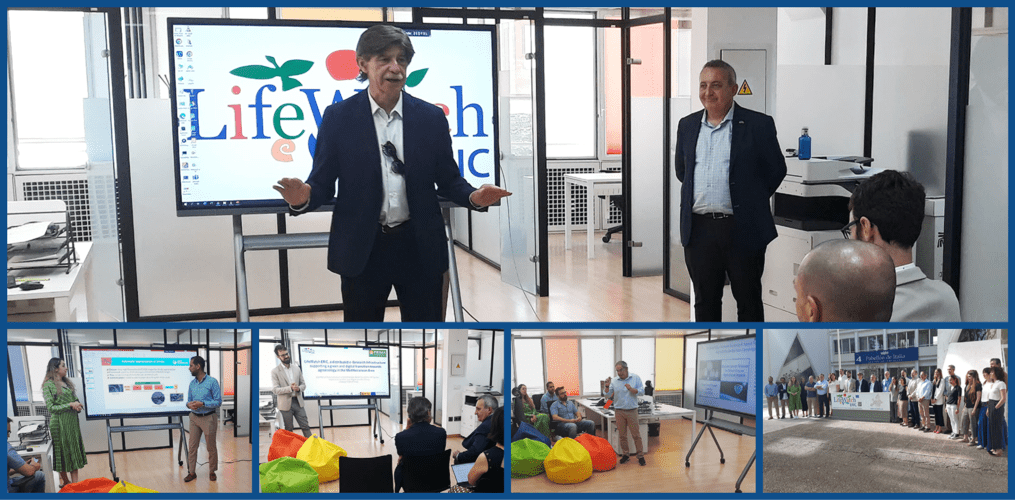
On 3–5 May, LifeWatch ERIC participated in the EOSC Future General Assembly and Project Meeting, held in Seville, Spain. The event was hosted by LifeWatch ERIC in Casa de la Ciencia, where all the entities who are the backbone of EOSC Future gathered.
Christos Arvanitidis, LifeWatch ERIC CEO, is very pleased with the level of participation and cooperation shown in the various sessions of this meeting: “Our assessment is very positive and increases expectations regarding the achievement of the objectives for the development of this platform”.
On the first day of the Meeting, LifeWatch ERIC’s CEO, Christos Arvanitidis, opened the first session by welcoming the participants and explaining the objectives of WP6, which is the Work Package coordinated by LifeWatch ERIC. Then Sally Chambers from Dariah (Digital Research Infrastructure for the Arts and Humanities) hosted the session “Onboarding and Integration: Challenges & Solutions”, indicating two main objectives:
- To clarify the differences between the five resource types which can be on boarded into the EOSC-Exchange;
- To explore the Resource Providers have faced when onboarding and integrating their resources into EOSC Exchange and use the methods of ‘user stories’ to explore how to ease the process.
The second part of the session was focused on “Implementing the Science Projects: Current status and next steps”, and was led by Cristina Huertas, LifeWatch ERIC International Initiatives and Project Manager. This second part of the session identified five main objectives:
- To identify the Risks of the technical implementation of Science Projects;
- To review the status of Scientific Documents;
- To explore the way Science Projects could consider their sustainability after the end of the project;
- To engage and satisfy the users;
- To review the status of the webinars provided by the ten Science Projects to date.
On the first day of the General Assembly, forty people have participated in person, in total, and other representatives of the consortium have also intervened livestream. Among others, Yannis Ioannidis, Greek delegate to the European Strategy Forum on Research Infrastructures (ESFRI), member of the ESFRI Executive Board, and ESFRI representative to the e-Infrastructures Reflection Group (e-IRG). As coordinator of EOSC Future, Yannis Ioannidis chaired the assembly. A total of thirty-five entities have also been integrated into the EOSC Future consortium.
The first day of EOSC Future General Assembly has been moderated by Ron Dekker, associate consultant at Technopolis Group Belgium (where he coordinates the Open Science activities) and EOSC Future Project Leader, and Lennart Stoy, senior consultant in Technopolis Group Belgium.
On the second day of EOSC Future General Assembly and Project Meeting, Agis Evrigenis and Sophie Viscido, from Technopolis Group, led the session dedicated to the overview of the project implementation status, challenges and next steps. Then Paolo Manghi (Openaire), Roksana Wick (ACK Cyfronet), Mark Van de Sanden (Surf / Eudat) and Klaas Wierenge (Géant), coordinated the session about new and upcoming tech capabilities and led a short presentation and demos by the product teams (marketplace, providers, portal, helpdesk, etc.). EOSC Architecture and Interoperability Framework has also been presented, discussing tech planning towards project end and capabilities to be demonstrated at the month 30 review.
LifeWatch ERIC, with Christos Arvanitidis, Cristina Huertas, and Ana Mellado, led a session about the overview status of Science Projects. The topics covered included: progress to date, resources’ integration status and plans, lessons learned as piloting EOSC and post project sustainability.
Later in the afternoon, LifeWatch ERIC presented a scientific case in progress: Implementation ARMS workflow. This early-warning system for marine biological invasions allows non native invasive especies (NIS) researchers and stakeholders to identify newly arrived NIS, track the migration of already known NIS and monitor the composition of hard-bottom communities over long periods. This system is based on ARMS data (Autonomous Reef Monitoring Structure), which are quality controlled and open access based, permanently stored (Marine Data Archive) along with their metadata (IMIS, catalogue of VLIZ), ensuring fairness.
LifeWatch ERIC CEO, Christos Arvanitidis, introduced Joaquín López Lérida, LifeWatch ERIC Data e-Science Management Plan & BlockChain Officer, who also explained, whit a remote online presentation, how the integration of the platform is being done with EOSC. In terms of authentication, the integration has been confirmed to be ready for internal consumption of all LifeWatch ERIC Tesseract Services, including LifeBlock.
In the session about real-life demonstrations of use cases, (in view of the month 24 review), which has been led by Matthew Viljoen, another of the presentations that has aroused interest is the one presented by Carolina Simón, from the National Center for Biotechnology (Spain), who exposed the case of integration of Covid-19 Data with EOSC. On the other hand, Elisa Cauhé (EGI Foundation), presented results and next steps of the EOSC Digital Innovation Hub (DIH): eight projects collaborations, twenty-three supported pilots, and more than fifty funding opportunities.
The last day of EOSC Future General Assembly and Project Meeting was, instead, focused on addressing aspects such as EOSC Procurement, EOSC as a Data Space and also RDA Open Calls. The closing session revolved around updates provided by WP10 about the progress made for the project.
The EOSC Future Meeting held in Seville for three days has concluded with a standing ovation from all the participants to congratulate the LifeWatch ERIC team for the quality of their work as host of the meeting.
Ron Dekker, EOSC Future Project Leader, called on all the entities participating in the consortium to intensify the implementation of their work packages, in order to finish the last phase of the project in the best possible way. From 20-22 September 2023, the EOSC Symposium will take place in Madrid, in the context of the Spanish Presidency of the Council of the European Union. In the context of the EOSC Future project, the EOSC Symposium will also be a critical platform to showcase project achievements and key exploitable results.