We are delighted to announce the collaboration between LifeWatch ERIC and OpenAIRE, aimed at advancing Open Science. By joining forces, we will enhance the accessibility of Open Science, improve the FAIRness of LifeWatch ERIC research and enrich the OpenAIRE Graph.
Open Science is gradually becoming the modus operandi in research practices, shaping the way researchers collaborate and publish, discover, and access scientific knowledge. Scientists are increasingly publishing research results beyond the article, to share all scientific products generated during an experiment, such as metadata, data, analytical services, etc.
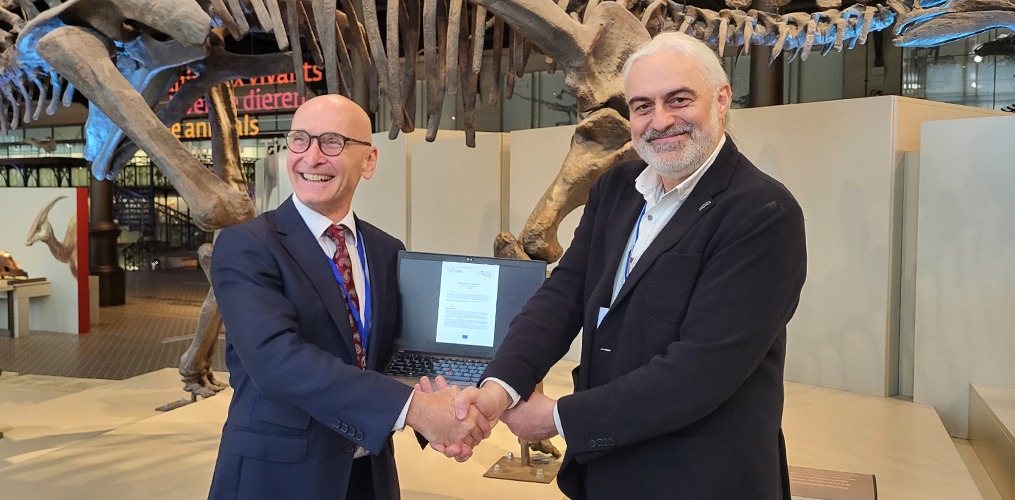
LifeWatch ERIC and OpenAIRE proudly signed a Memorandum of Understanding to sustain and accelerate Open Science. They commit to enhance their Open Science activities by improving the FAIRness of the LifeWatch ERIC research and enriching the OpenAIRE Graph. Both organisations have joined forces to work on EOSC projects, with the OpenAIRE Graph playing a crucial role in aggregating data sources and connecting metadata such as funding information, data, publications, software, and other unique identifiers (PIDs). Through this collaboration, the combined efforts of Lifewatch ERIC and OpenAIRE will enhance the overall data quality presented on the EOSC Portal.
As a result of this collaboration, all publications, datasets, research projects, software and other outputs of LifeWatch ERIC will now be made accessible through an OpenAIRE CONNECT gateway. Moreover, a MONITOR service with a set of configurable indicators and tools will be made available to simplify research monitoring and evaluation, while measuring and increasing the uptake of Open Science practices.
Sustaining flagship project outputs that provide the infrastructural backbone of FAIR (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable and Reusable) and open data discovery is a priority to both organisations. These efforts will also play key role in realising a meaningful European Open Science Cloud for research communities, building upon the work that is already undertaken in other projects, such as EOSC-FUTURE, FAIR-IMPACT, BioDT and OpenAIRE Nexus project.
“Providing access to the world’s biodiversity content, services and communities in one click is LifeWatch ERIC’s vision. The signature of this Memorandum of Understanding is yet another milestone to this direction, by fostering synergies and complementing each other, both OpenAIRE and LifeWatch ERIC will have a more significant impact and valuable contribution to the acceleration and integration of Open Science and FAIRness within the European Research Area and beyond, providing even more innovative and interoperable tools for our research communities”, Christos Arvanitidis, LifeWatch ERIC Chief Executive Officer.
“This partnership aims to bring together the biodiversity communities closer to Open Science in practical ways, through shared infrastructure, bringing economies of scale, and building trusted relationships. OpenAIRE can only learn from LifeWatch ERIC so as to calibrate our services to respond to the real needs of this vibrant community”, Natalia Manola, OpenAIRE CEO.
About:
LifeWatch ERIC: LifeWatch ERIC is a European Research Infrastructure Consortium providing e-Science research facilities and services to scientists investigating biodiversity and ecosystem functions in order to support society in addressing key societal challenges linked to climate change and resource efficiency, food security and agriculture, sustainable development, energy and health. LifeWatch ERIC’s vision is to become the Research Infrastructure providing access to the world’s biodiversity content, services and communities in one click.
OpenAIRE: OpenAIRE is a Non-Profit Partnership, established in 2018 as a legal entity, OpenAIRE AMKE, to ensure a permanent open scholarly communication infrastructure and support research in Europe and beyond. OpenAIRE is making Open Science happen. Collectively and in practical ways. Its fields of expertise and activities include services, policies and training. Operating since 2009, OpenAIRE is an integral part and a leading force behind the European Open Science Cloud developments.
OpenAIRE Nexus: The Horizon 2020 OpenAIRE-Nexus project, a consortium of 11 partners, brings in Europe, EOSC and the world a set of services to implement and accelerate Open Science and tools to embed in researchers’ workflows, making it easier for them to accept and uptake Open Science practices of openness and FAIRness.