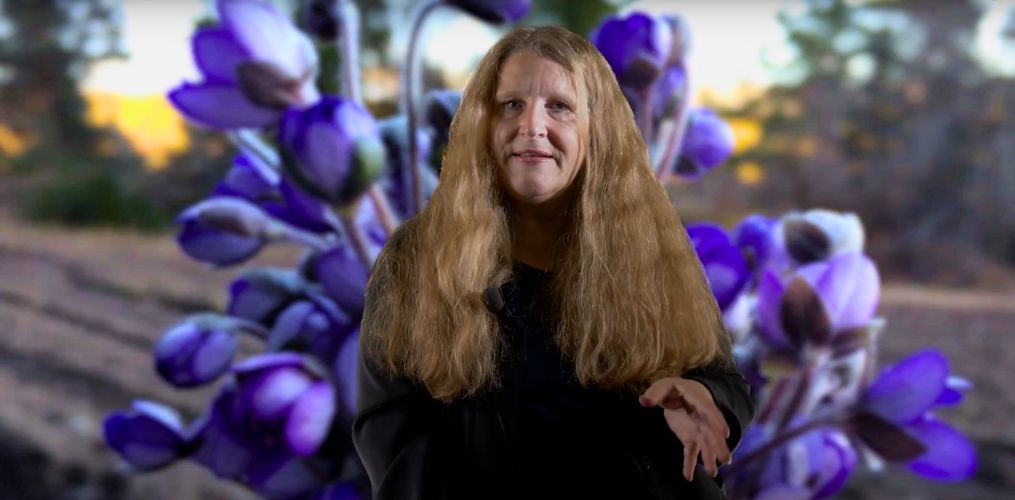
“As a little girl, I was roaming around in the forest in spring, enjoying the fact that the snow had melted.
I grew up in Norway; we have long winters and looking for the spring flower was one of the favourite activities for kids…And looking for Epatica nobilis (Liver leaf) was one of the most important things we did because we got to get in the local newspaper if you were the first ones. We knew about specific places where the snow melted first and we had some hints of leaves etc that indicated that this is the place where we could find this precious flower.”
Remember searching for the first spring flowers as a child?
In our third BioDT Talks episode, Bente Lilja Bye, founder of the research and consulting company BLB, shares how her childhood quests for Hepatica nobilis in Norway and her mother’s meticulous nature diaries evolved into groundbreaking work in biodiversity data science!
The information about the first Epatica nobilis of the year and the “metadata” around these spring flowers, carefully handwritten in her mother’s diary, were her first experience collecting data, and the first repository of her life. An important channel for her to get involved in her current job.
In her talk, Bente Lilja Bye explains in particular why is worth learning about data pipelines and to build Digital Twins for biodiversity.
So, first of all, what is a Digital Twin? A Digital Twin for biodiversity is a sophisticated digital representation of ecosystems, species, and their interactions with the environment. This technology integrates various data sources to create a dynamic simulation that mirrors real-world biological systems. “A simple representation of a Digital Twin is that you have a physical system and a virtual system”, Bente Lilja Bye says. “Data or observations of the physical system are used to create the virtual system. Now, the virtual system is running models etc giving feedback into the physical system and in this way we have a loop called Digital Twin”.
The data is the core of a Digital Twin, we would not have Digital Twins without data. There are currently many sources and many types of data, and the challenge is to collect, harmonise, standardise, processing all this amount of information to put all these different types of data together. Data pipelines are essential for efficiently processing vast amounts of data and providing real-time insights for Digital Twins. In simpler words, they are systems leading from the collection and acquisition of data, to their final transformation into new knowledge or possible decisions. Moreover, data pipelines enable industry, academia, and the public sector to more efficiently share data, facilitating interdisciplinary collaboration.
“By being a foundational component of a Digital Twin, a data pipeline represents a transformative approach to biodiversity conservation, offering enhanced monitoring capabilities, improved decision-making processes, predictive insights, and fostering collaboration among stakeholders. And these benefits are instrumental in addressing the pressing challenges facing global biodiversity today”.
Watch the video, and find out how we can transform data into new knowledge.
BioDT is a research project funded by the European Union that aims to develop a digital twin prototype for the study and analysis of biodiversity, in support of the EU Biodiversity Strategy for 2030. The Biodiversity Digital Twin prototype provides advanced models for simulation and prediction capabilities, through practical use cases addressing critical issues related to global biodiversity dynamics.
The BioDT Talks is the new 6-part series illustrating how data science and technology are transforming our approach to the biodiversity crisis.
More information on the BioDT Project HERE.
Watch the full playlist on YouTube and find out more!