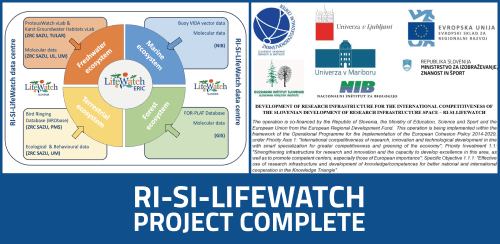
In December 2019, the “Development of research infrastructure for the international competitiveness of the Slovenian RRI space – RI-SI-LifeWatch” project was granted by the Slovenian Ministry of Education, Science and Sport and the European Regional Development Fund. The aim of the project was for the LifeWatch Slovenia consortium to build a network for monitoring and collecting biodiversity and environmental data obtained and processed through the acquisition of high-performance research equipment.
With the help of the new research equipment from the RI-SI-LifeWatch project, the Slovenian consortium is now collecting a large amount of research data in digital form, which will be included in the national Karst database, harmonised with FAIR principles and designed to provide a temporal and spatial link between specific sites.
The LifeWatch Slovenia Data Centre has also been established and consists of very powerful server and computer units. Although it is still in an early stage of development, the current functionality of LifeWatch Slovenia Data Centre is beginning to collect the various large datasets obtained with the new instruments and catalogue their metadata within a GeoNetwork portal to build a standardised database with system management and user interface for data mining and access to data products. The architecture of the new data centre proposes to replicate the functionality and standards of LifeWatch ERIC to be compliant with FAIR data principles and data lifecycle. Data collected by RI-SI-LifeWatch’s equipment will support the development of data and services planned and/or already developed and operating within the LifeWatch Slovenia consortium.
In addition, LifeWatch Slovenia is now providing new ecological research measurements and observations leading to scientific publications, as well as new datasets for the Bird Ringing database (BRDbase), for the FOR-PLAT forest database and for the Buoy VIDA marine database.
With the new equipment we will develop two virtual labs in the near future: ProteusWatch vLab, Karst Groundwater Habitats vLab to assess and monitor the inaccessible and unique karst groundwater biodiversity hotspots (e.g. Proteus anguinus and various cave invertebrates).
The RI-SI-LifeWatch project has also enriched the international research infrastructure LifeWatch ERIC with new research opportunities and incentives. The project has helped to:
- conduct modern biodiversity research for marine, freshwater, and terrestrial ecosystems
- establish open access to Big Data related to various databases and observatories
- conduct data visualisation from virtual labs with modelling tools and enhance the LifeWatch RI by developing new analytical capacity for open research data
- support targeted user training and collaboration to monitor and predict the impacts of global change on biodiversity
A national hub of distributed biodiversity and ecosystem research data centres will be implemented at individual national partners. The RI-SI-LifeWatch project was successfully completed on 31 August 2021.